1. 简介
JMX(Java Management Extensions)是 Java 提供的一种用于管理和监控应用程序、系统对象及资源的技术框架。它通过 MBean(Managed Bean)实现对资源的动态管理,支持远程监控和配置调整,广泛应用于性能调优、故障排查和运维管理场景。
1.1 JMX 的核心价值
- 运行时管理:无需重启应用即可调整配置参数
- 性能监控:实时查看应用状态和性能指标
- 故障排查:通过JMX工具快速定位问题
- 运维自动化:支持脚本化管理和监控
2. 基本使用
结合 Spring 可以便捷使用:
相关注解:
org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedResource - 标记MBean类org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedAttribute - 标记属性org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperation - 标记操作org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperationParameters - 标记操作参数org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.ManagedOperationParameter - 标记单个参数
在Spring Boot应用中,需要启用JMX支持:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: "*"
endpoint:
jmx:
enabled: true
|
或者通过JVM参数启动:
1
2
3
4
| -Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.port=9999
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.authenticate=false
-Dcom.sun.management.jmxremote.ssl=false
|
2.1 MBean
2.1.1 MBean 介绍
MBean(Managed Bean)是 Java 平台中用于管理应用程序组件的一种机制,属于 Java Management Extensions (JMX) 技术的核心部分。MBean 是一种标准的、可被管理的 Java 对象,
它通过暴露属性和操作来允许外部管理系统(如 JConsole 或其他监控工具)与其交互。
2.1.2 定义一个 MBean
在 Spring 框架中定义一个 MBean 非常方便,使用 ManagedResource 注解,并将目标类注册为 Bean 即可,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
| package com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
@ManagedResource(
objectName = "com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx:name=DataManager",
description = "数据管理MBean,提供数据存储和统计功能"
)
@Component
public class DataManager {
private final Map<String, String> data = new HashMap<>();
private final AtomicLong accessCount = new AtomicLong(0);
private boolean enabled = true;
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取访问次数")
public long getAccessCount() {
return accessCount.get();
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取启用状态")
public boolean isEnabled() {
return enabled;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "设置启用状态")
public void setEnabled(boolean enabled) {
this.enabled = enabled;
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "重置访问计数器")
public void resetAccessCount() {
accessCount.set(0);
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "获取数据大小")
public int getDataSize() {
return data.size();
}
}
|
Spring 会自动将其注册为 MBean,并暴露出去。
2.2 MBean Attribute
2.2.1 MBean 属性是什么
MBean 的属性是指该 MBean 中可以被外部访问或修改的状态信息。这些属性通常以 Java 类中的字段形式存在,并通过一组标准化的 getter 和 setter 方法对外暴露。MBean 属性的设计目的是让外部管理系统能够读取或更新 MBean 的状态,而无需直接访问其内部实现。
属性的特点
- 命名规范:
- 属性名称必须遵循 JavaBeans 命名规范。
- 例如,如果属性名为
CacheSize,那么对应的 getter 方法应为 getCacheSize(),setter 方法应为 setCacheSize(int value)。
- 只读或可写:
- 如果只有 getter 方法,则该属性是只读的。
- 如果同时有 getter 和 setter 方法,则该属性是可读写的。
- 数据类型:
- 属性的数据类型可以是基本类型(如
int、boolean)或复杂类型(如自定义类)。
- 复杂类型的属性需要确保其类是可序列化的,以便在分布式环境中传递。
- 元数据描述:
- 每个属性可以通过 JMX 提供的元数据进行描述,例如属性的名称、类型、描述信息等。这些元数据可以帮助管理工具更好地理解和展示属性。
2.2.2 示例:定义一个简单的 MBean 及其属性
以下是一个简单的 MBean 示例,展示了如何定义和暴露属性:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
| package com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@ManagedResource(
objectName = "com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx:name=ConfigManager",
description = "配置管理MBean示例"
)
@Component
public class ConfigManager {
private String appName = "JMX Demo App";
private String version = "1.0.0";
private boolean debugMode = false;
private int maxConnections = 100;
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取应用名称")
public String getAppName() {
return appName;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "设置应用名称")
public void setAppName(String appName) {
this.appName = appName;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取应用版本(只读)")
public String getVersion() {
return version;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取调试模式状态")
public boolean isDebugMode() {
return debugMode;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "设置调试模式")
public void setDebugMode(boolean debugMode) {
this.debugMode = debugMode;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "获取最大连接数")
public int getMaxConnections() {
return maxConnections;
}
@ManagedAttribute(description = "设置最大连接数")
public void setMaxConnections(int maxConnections) {
if (maxConnections > 0) {
this.maxConnections = maxConnections;
}
}
}
|
在这个示例中:
version 是一个只读属性,因为只有 getVersion() 方法。appName、debugMode、maxConnections 是可读写属性,因为它们既有 getter 方法,也有 setter 方法。
2.3 MBean Operation
MBean 操作(MBean Operation)是 MBean 暴露给外部系统的可调用的方法。这些方法允许管理员或监控系统在应用运行时执行特定的管理性任务,比如清空缓存、重启服务、重新加载配置等。
在 Spring 中,使用 ManagedOperation 注解标注,使用 ManagedParameters 注解标记操作接收的参数,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
| package com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx;
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import org.springframework.jmx.export.annotation.*;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
@ManagedResource(
objectName = "com.mk.jmxdemo.jmxdemo.jmx:name=DataManager",
description = "数据管理MBean,提供数据存储和统计功能"
)
@Component
public class DataManager {
private final Map<String, String> data = new HashMap<>();
private final AtomicLong accessCount = new AtomicLong(0);
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
data.put("name", "maphicalyng");
data.put("age", "18");
data.put("gender", "male");
data.put("email", "maphicalyng@example.com");
data.put("phone", "1234567890");
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "获取指定数据")
@ManagedOperationParameters(
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "key", description = "数据键")
)
public String getDataKey(String key) {
accessCount.incrementAndGet();
return data.get(key);
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "设置指定数据")
@ManagedOperationParameters(
value = {
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "key", description = "数据键"),
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "value", description = "数据值")
}
)
public void setDataKey(String key, String value) {
data.put(key, value);
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "清空所有数据")
public void clearAllData() {
data.clear();
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "获取所有数据键")
public String[] getAllKeys() {
return data.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
}
@ManagedOperation(description = "批量设置数据")
@ManagedOperationParameters(
@ManagedOperationParameter(name = "dataMap", description = "数据映射(JSON格式)")
)
public void batchSetData(String dataMap) {
}
}
|
其中:
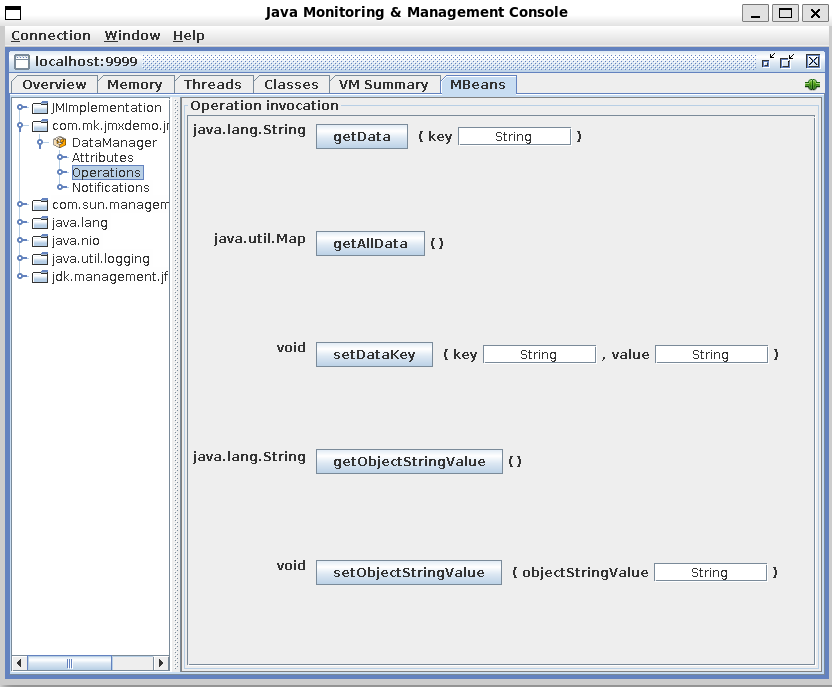
getDataKey 和 setDataKey 是两个 Operation,用于查看和设置 data 的特定 key 的值clearAllData 用于清空所有数据getAllKeys 用于获取所有数据键batchSetData 用于批量设置数据
在 jconsole 等外部工具中,会显示为一个按钮,并提供输入控件来输入调用参数,点击执行后,会执行对应 Operation 方法中的逻辑。
3. 相关工具
3.1 jconsole
JDK 自带的图形化工具,用于通过 JMX 管理 Java 系统。
上述 MBean 在 jconsole 中的操作界面为:
总览
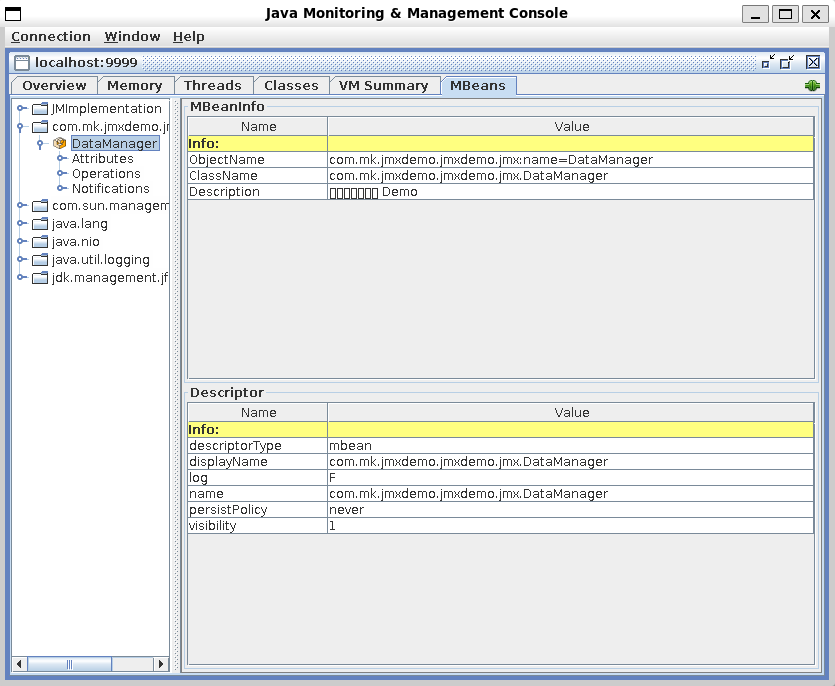
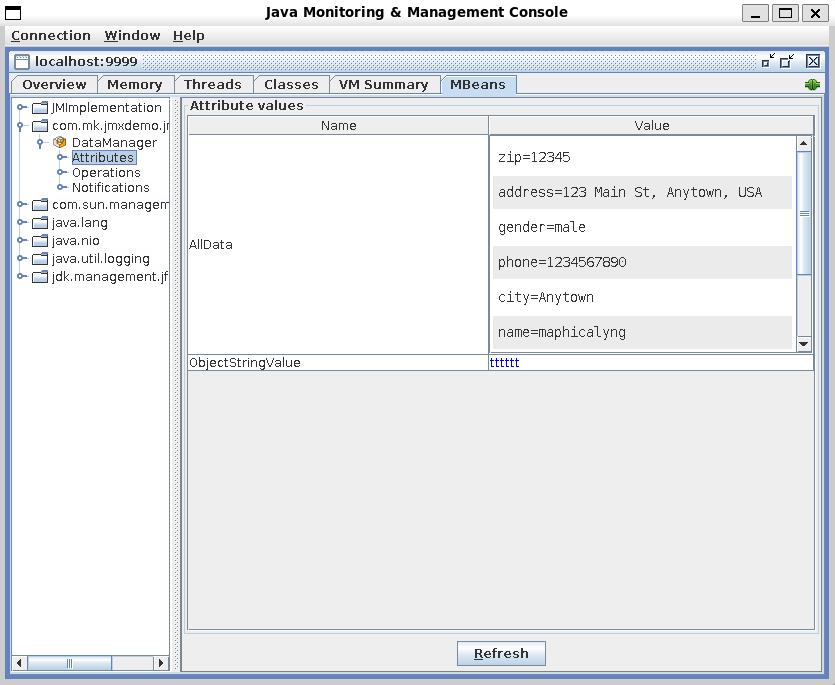
Attributes
Operations
Notifications
3.2 jmxterm
开源的 JMX 命令行管理工具,当在无图形界面的环境中连接 JMX 时使用,项目地址:
CYCLOPSGROUP DOCS - Jmxterm
使用示例:
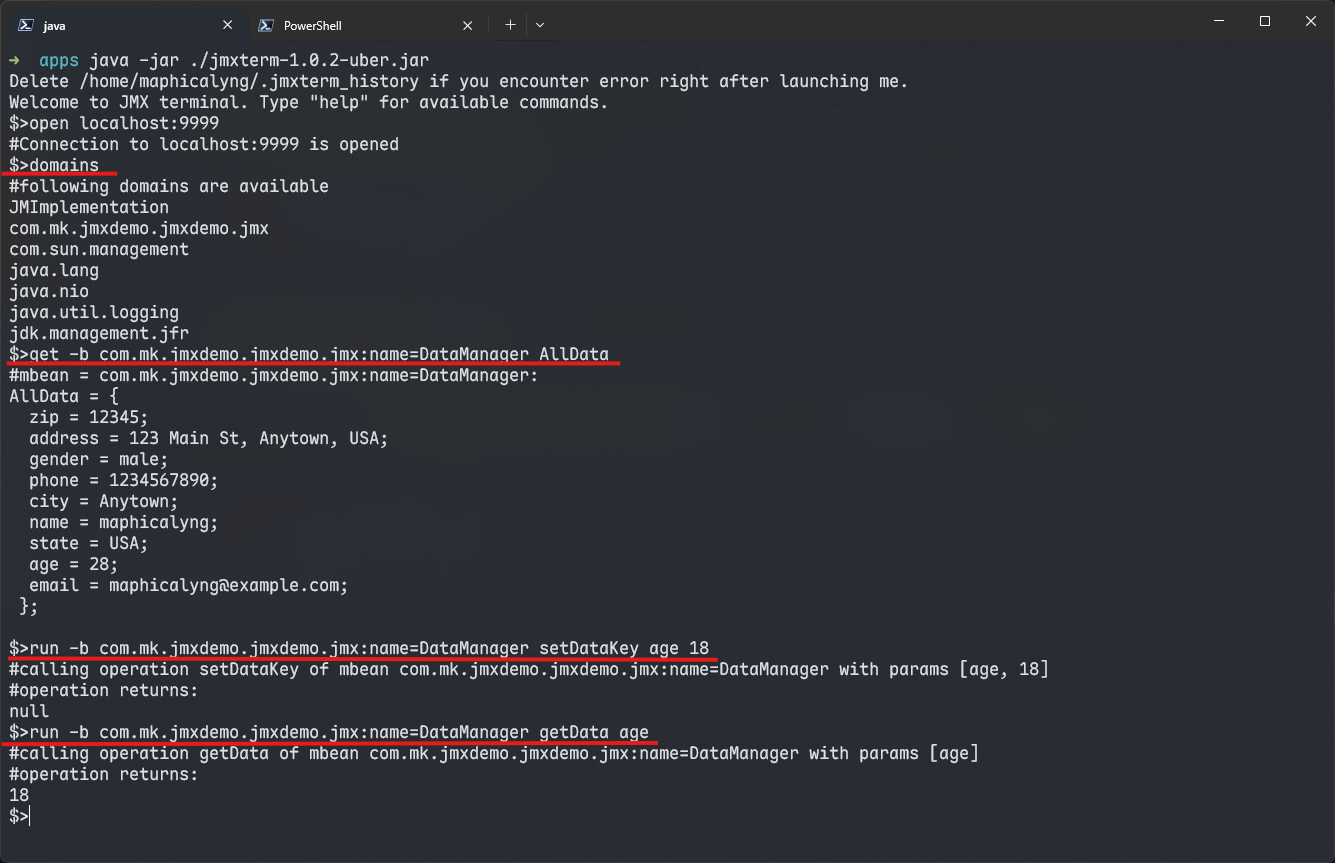
四条命令的说明:
- 列出所有 MBeans 的 domain;
- 获取 Attribute 的属性值;
- 调用 Operation setDataKey,参数为 age、18;
- 调用 Operation getData,参数为 age。
4. 最佳实践和注意事项
4.1 性能考虑
- 避免频繁调用:JMX 操作会消耗系统资源,避免在高频场景下使用
- 线程安全:确保 MBean 的属性和操作是线程安全的
- 异常处理:在操作中妥善处理异常,避免影响主业务逻辑
4.2 安全考虑
- 权限控制:生产环境中应该启用 JMX 认证和 SSL
- 敏感信息:避免在 JMX 中暴露敏感配置信息
- 网络隔离:限制 JMX 端口的网络访问
4.3 监控建议
- 关键指标:监控应用的核心业务指标
- 告警机制:结合监控系统设置合理的告警阈值
- 日志记录:记录重要的 JMX 操作日志
4.4 常见问题
- 连接失败:检查 JMX 端口配置和防火墙设置
- 权限不足:确认 JVM 参数中的认证配置
- 性能影响:避免在性能关键路径上使用 JMX
以上。




